
POP does have a few advantages for those who choose to use it. This speeds up your ability to go through your email messages, as you don’t waste time downloading attachments you have no desire to see.īecause POP is a slightly older technology than IMAP, your email client may be set up to use POP, even if you don’t know it.
#GSUITE IMAP SETTINGS FOR MAC MAIL DOWNLOAD#
If you are checking email messages that have attachments with them, when you have IMAP activated, any attachments to those emails will not download until you attempt to open them. With IMAP, the device only downloads a copy of the contents of an email message when you click on it to read it. Because you do not have to wait for all of your new messages to download to your device each time you sign into the email server when using IMAP, your overall email experience will seem faster. The server will maintain a record of all messages you sent for a period of time. If you have deleted messages that you need to access again later, or if you just need to verify that a message was actually sent, using IMAP may allow you to find an old message. The messages do not download to any one device. As long as you have an Internet connection available, you can see your email messages from any device and wherever you are. IMAP is the preferred protocol for the majority of users, as it carries quite a few advantages. Copies of these folders and your organizational structure will not appear on the email server, as they do with IMAP. When organizing and sorting your emails through POP, the folders will only appear on your local device. At the time of the download, the email server nearly always deletes the message from the server, meaning the only copy is now on your device. When you set up POP for your email client, your messages download automatically to your device from the email server.

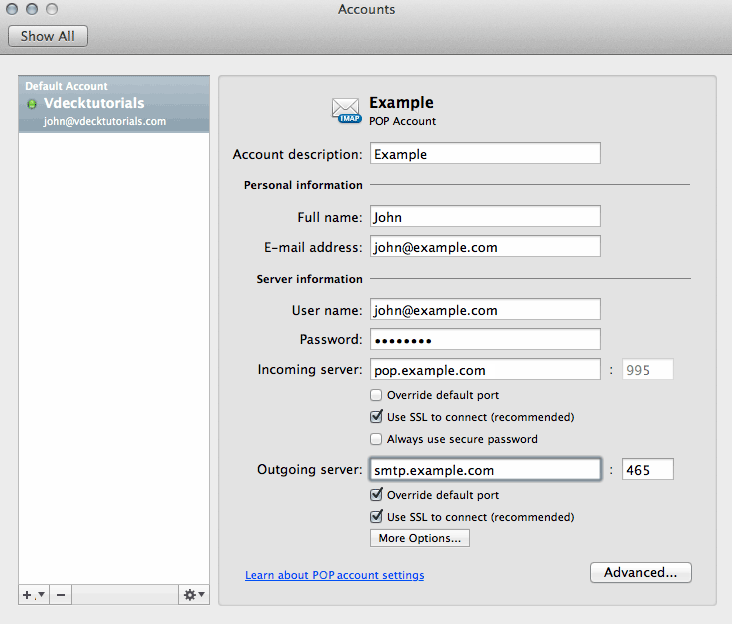
What Is POP?īefore we compare IMAP and POP, let’s discuss how POP works. You can even switch between the two protocols as much as you want, if that would fit your desired use case better. The majority of email clients can use both IMAP and POP, and you can set up the client to use the one you prefer. These protocols are not interchangeable and do not mean the same thing. POP: Which Is Better?Įven though IMAP and POP both deal with managing email messages, they work in significantly different ways.
Any changes you make while the message is on your device become mirrored on the email server through the IMAP protocol.Īs an added advantage, you can sort and organize your email messages using IMAP without ever having to download them to your device.Īs long as you have a secure and fast connection to the email server, you will be able to work quickly when using IMAP.
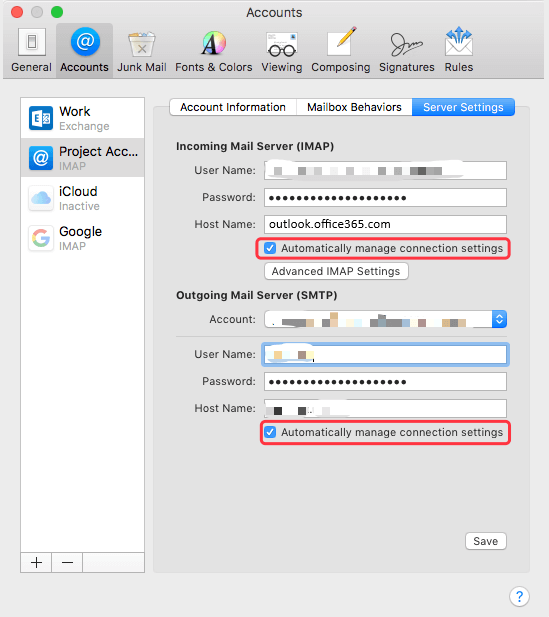
The IMAP middleman synchronizes the messages on both your device and on the email server. IMAP gives you the ability to see and manage the emails, while leaving them stored on your email server. You can think using IMAP like employing a middleman to manage your email messages. Without IMAP, your messages would be stuck on the first device where you downloaded them, meaning you could not access them from a mobile device later. You don’t remove the messages from the server when you download the email messages to your computer. The advantage of IMAP is you can open your email messages from any device that is logged into your email client. When you open them to read them, your email client leaves the original copy stored on the server, just allowing you to see a copy of the content in the message. With IMAP, you do not automatically download the email messages from the server to your device. Its primary function is to give you the ability to control how your email messages move from your email server to your client software. IMAP is short for Internet Message Access Protocol. Here are the settings you will use to configure IMAP for your preferred desktop client to handle incoming Gmail.
#GSUITE IMAP SETTINGS FOR MAC MAIL HOW TO#
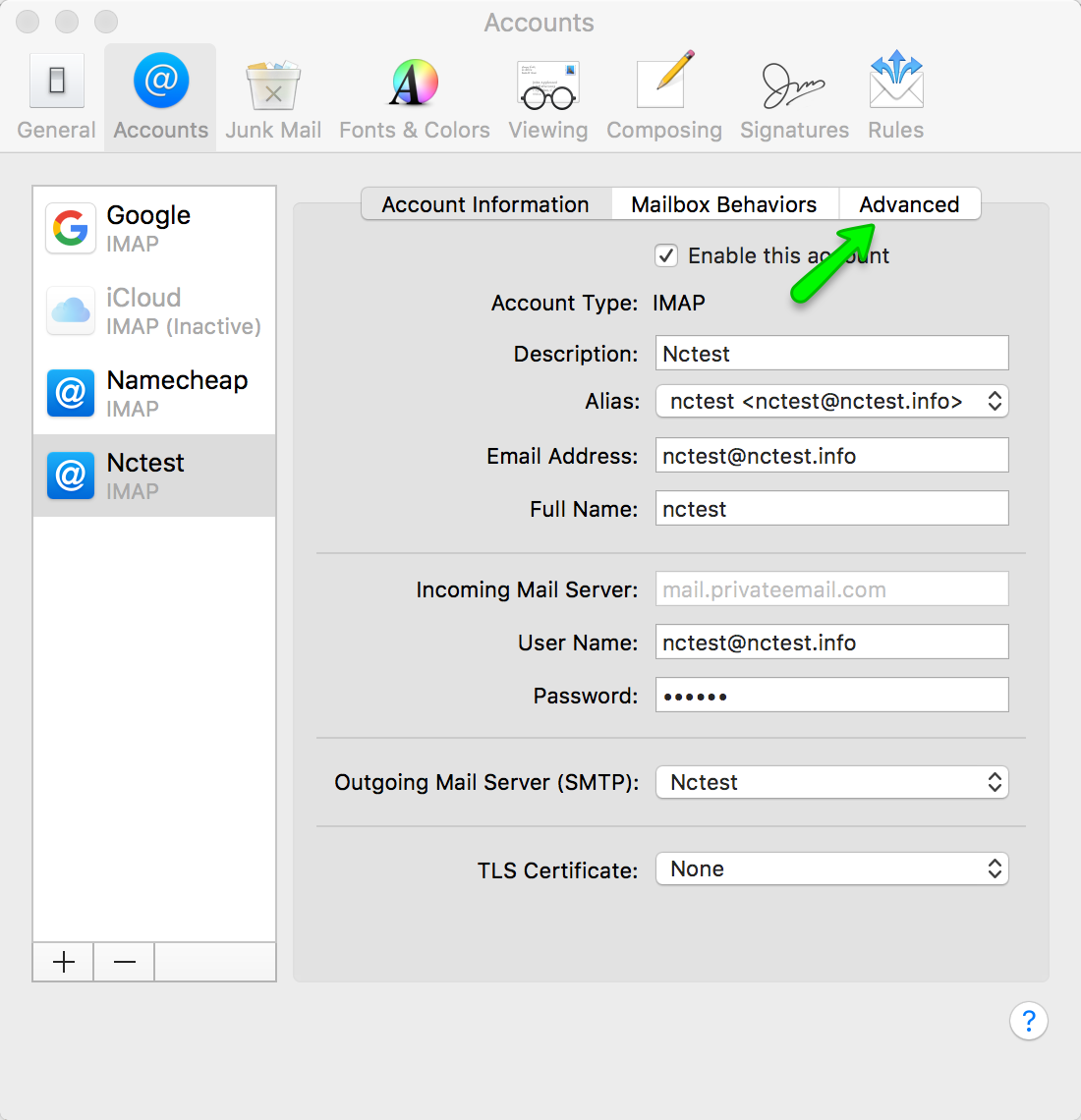
We’ll help you figure out how to make the most of the G Suite IMAP settings. By making changes to these settings, you easily can manage with your emails in the desktop client that you prefer. If you’re interested in making use of Microsoft Outlook, Apple Mail, or other desktop clients with G Suite and Gmail, you will need to learn about the IMAP settings in G Suite. Although the G Suite mail interface is easy to navigate, some people prefer to use a different email client to handle messages they receive through G Suite, gaining a few more features.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
